Data shows that user-centric designs increase engagement rates with users and result in more conversions and sales. Whether you’re designing a website's landing page, a physical product, or even a billboard ad, you cannot afford to ignore user-centric designs. Doing so could create friction with users and result in lower sales.
Luckily, today, companies have access to a large pool of tools that offer accurate data-driven insights along with techniques to help them create the perfect user-centric design. Here, we break down everything you need to know about modern user-centric designs along with benefits and highlight some examples that can help you with your own approach.
Definition of User-Centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) is a design philosophy and technique that prioritizes the user in the design and development process. This means crafting an approach that prioritizes the needs, wants, and limitations of end-users so that the final product is tailored to meet their expectations and improve their overall experience and interaction.
With this approach, every stage of the design process, from initial research and development to prototyping and user testing, focuses on the user’s feedback and interaction. The goal is to create products that are user-friendly and accessible, in addition to just being functional.
User-Centric vs. Product-Centric Approaches
A user-centric design approach is different from a ‘product-centric’ approach. Here’s how:
- User-Centric Design (UCD): This approach centers the product on fitting the user's needs and preferences. It also involves understanding the users' context, behaviors, and challenges to design intuitive and easy-to-use solutions. UCD aims to enhance the user's experience by making products more accessible and enjoyable.
- Product-Centric Design: In contrast, a product-centric approach focuses on the product capabilities and technology available rather than how ‘user-friendly’ the design is. The product-centric model tends to force users to adapt to the product and has a learning curve attached to it. This can often result in friction between the product and the user.
User-Centered Design: A Continuous Process
User centered design is not just a methodology but a continuous improvement process. It involves several iterative steps that help refine the product based on user input:
- Research: Understanding user needs, behaviors, and environments through interviews, observations, and surveys.
- Design: Develop prototypes that incorporate user feedback to address their needs effectively.
- Testing: Conducting usability tests with real users to gather insights about the product’s performance and the user's interaction with it.
- Refinement: Adjusting designs based on testing feedback may cycle back to further research and testing as needed.
Key Principles of User-Centric Design
Key design principles for UCD include:
- Empathy (Connecting with user feedback): This approach focuses on understanding users' experiences, needs, thought processes, and emotions. By empathizing with users, designers can create solutions that resonate and meet real-world requirements. This can help ensure the product or service is genuinely useful and relevant.
- Participatory Design (integrating user feedback): This approach involves integrating user feedback directly into the design process. Designers can get insights directly from the target audience via workshops, focus groups, and usability testing techniques. This enhances the relevance and usability of the design. It also empowers users, giving them a voice in developing solutions that affect them.
- Iterative Process (Adapting to changing preferences): This approach is a cyclical process of designing, testing, and refining. This continuous loop allows designers to adjust based on real user feedback and testing outcomes.
Each iteration aims to improve the previous version, producing a more polished and user-friendly final product. This ensures the design evolves closely with the users' changing needs and preferences.
User-Centered Design vs. Traditional Design Approaches
User-centric design is a fairly new design philosophy that has emerged as an alternative to the traditional design approach. Here’s how both are different:
- Design Focus: User-centered design (UCD) prioritizes users' needs, behaviors, and experiences. The product is made to maximize user engagement by ensuring user-friendliness and satisfying user interaction.
In contrast, the traditional design approach emphasizes product capabilities, focusing on form and function from a more technical perspective. There’s little direct consideration of user engagement with the product involved.
- Feedback Loop: UCD involves a continuous feedback loop, incorporating user input at multiple stages through various techniques such as testing, interviews, and usability studies. This iterative process allows the product to be refined based on actual user experiences, making the final product more aligned with user needs.
In contrast, traditional design methods follow a more linear progression. The process moves from concept to completion without extensive iteration or re-evaluation based on user feedback.
- Outcome Metrics: The primary metrics that measure a product’s success with UCD are user satisfaction and usability. How well the product meets user expectations and facilitates ease of use is closely tied to its ultimate success.
In contrast, the traditional design approach might measure success by technical performance, focusing on how well the product meets predetermined technical criteria rather than its impact on user experience.
Of course, designers can always look to strike a balance between the traditional design approach to create technically efficient products while keeping a user-centric design approach to increase user interaction and engagement.
The Role of User Research in User-Centric Design
Poor data leads to poor decision-making. The same is true when we consider the importance of user centered design, especially where understanding the user is central to your design strategy. User research and creating a user centered design framework are the backbone of great user-centric design. For effective research, you need two things: the right tools and the right techniques.
As far as user centered design techniques go, you have multiple ways to gain actionable insights. You can use observational studies to track user behavior in natural settings and get an unfiltered reaction to the product. Interviewing users is also effective because you can extract detailed opinions and feelings about the user experience. Another user centered methodology is using contextual inquiries, where you blend observation and interviews to examine how users interact with a product in their typical environments.
The insights derived from user research inform every stage of the design process.
Initially, they help define precise user requirements. This ensures that the product concept aligns closely with user needs. As the design evolves, more user feedback guides iterations and helps guide future product development. Post-launch, ongoing user research provides real-time data on
how users interact with the product and what can be improved.
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20Image%201%20(22).png)
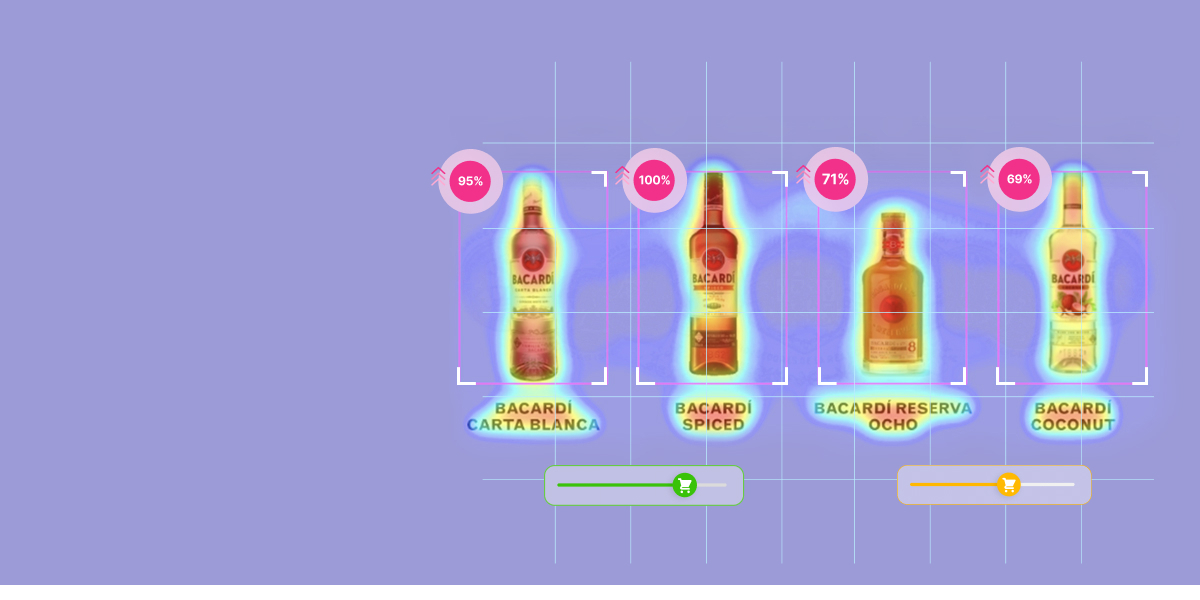
As far as tools go, check out Dragonfly. The platform’s AI capabilities enhance traditional user research by predicting where users will likely focus their attention within a specific area. The tool uses data-driven analytics to highlight areas likely to engage users, allowing designers to refine user interfaces. This can help optimize them for better user interaction and satisfaction before conducting live testing.
Analyzing User Data to Inform Web Design
Modern web design is a prime example of an area where user-centric design serves as the foundation. If a website’s design is not optimized according to modern UI/UX design, it can cause most site visitors to leave without taking any meaningful action.
Modern websites also have various tools and techniques at their disposal to analyze user data to inform web design. This can ensure optimal user engagement rates, lower bounce rates, and higher conversions. Here’s how:
- Behavioral Analytics
With behavioral analytics, you examine user interactions, such as click patterns, navigation paths, and interaction rates, to design user-friendly interfaces. By understanding how users navigate patterns within a website, designers can identify pain points and optimize the user experience.
For example, if data shows that users frequently abandon their carts at a certain step, designers can streamline that part of the process to reduce bounce rates and increase conversions.
- Heatmaps and Attention Analysis
Tools like Dragonfly AI offer heatmaps and attention tracking. With heatmaps, you can visually track the most and least engaging elements of a web design. Heatmaps show where users click, scroll, and spend the most time.
They provide insights into which areas capture attention and which are most ignored by users. This helps designers prioritize content placement and enhance overall engagement by focusing on the elements that most appeal to users.
- A/B Testing
A/B testing tests design variations by splitting users into groups and showing each group a different webpage version. By analyzing the performance of each version, such as click-through or conversion rates, designers can determine which design is more effective. This data-driven approach can help make decisions based on user preferences and behavior, leading to more user-centric web designs.
Evaluating User Experience (UX) in User-Centric Design
To ensure the design effectively meets user needs, you need to quantify and evaluate the user experience. A user centric definition of evaluating user experience entails the following:
- Usability Testing: This involves creating scenarios based on typical user tasks to evaluate the design's effectiveness. These scenarios replicate real-world tasks users might perform, allowing designers to observe how easily and efficiently users can complete them. Feedback from usability testing helps identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- User Satisfaction Surveys: Direct user feedback through satisfaction surveys is crucial in gauging the design's success. These surveys ask users about their overall experience, ease of use, and satisfaction with specific features. The insights gathered help designers understand whether the design meets user expectations and needs, which helps with further enhancements.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Using real-time data and tools like Dragonfly AI enables immediate adjustments based on user interactions. Dragonfly AI analyzes user behavior and provides insights into how users navigate and interact with the product or service. This real-time feedback allows designers to quickly address issues, optimize user pathways, and enhance the overall user experience on the go.
Examples of Successful User-Centric Design Projects
Some examples of successful user-centric design projects include:
Gaiam, a wellness e-commerce site, faced a UI/UX issue: Customers were abandoning their carts and not completing their purchases. The store went on a mission to find out what was causing this friction. Research revealed four key reasons:
- Customers would compare prices with other websites
- Shipping costs on the checkout were unclear
- Compared to other platforms, Gaiam offered low incentives
- The mobile checkout experience for many users was ideal.
An A/B test was conducted to see which checkout menu most appealed to users. Results showed that the design in the second image was more appealing and reduced many of the issues initially identified. Implementing the new menu resulted in a 13% drop in cart abandonment.
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%202%20(21).png)
A dating app faced the challenge of retaining users despite a strong initial download rate. To address this, the app focused on optimizing the user experience (UX) through feedback and leveraging App Store Optimization (ASO) strategies.
The app actively encouraged satisfied users to leave positive reviews, monitored feedback, and responded to user concerns, building trust and credibility. It also revamped its onboarding process to get users to provide more feedback about what they were looking for and themselves. This was used to tailor their profiles better and provide relevant recommendations.
The app remarkably increased user retention and conversion rates by implementing these user-driven improvements. This led to a 430% increase in retention rates and enhanced user reviews.
Sephora implemented user-centric design in its digital kiosks and shopping apps, leveraging AI to offer personalized recommendations. Through the virtual artist app and in-store kiosks, the company tailored product suggestions based on customers' skin tones and preferences.
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%203%20(20).png)
This user centric design approach helped enhance the shopping experience by providing individualized assistance and increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. The seamless integration of AI across customer touchpoints has increased engagement and boosted online and in-store sales.
Future Trends and Challenges in User-Centric Design
How people interact with any design around them is always evolving. Product-centric designs might have worked historically, but they are no longer usable simply because people have gotten accustomed to user-centric designs. Users today expect designs to be centered around them, and anything less directly impacts a company’s revenue and growth.
With new technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR), and Augmented Reality (AR) now in the mix, consumer interaction with design is destined to change and become more personalized and immersive. The only way to keep this is to embrace the user-centric design philosophy.
Of course, as this area evolves and the available products become more diverse, the challenges also grow. Companies will find it harder to scale their research and test different elements of the design process to keep up with user satisfaction. Privacy and ethical challenges will also grow, and companies must keep up in a world where users grow more concerned about their privacy.
This is why tools like Dragonfly AI can be an answer. As a leading creative intelligence and optimization platform, we use cutting-edge technology to provide clients with data-driven design insights. We do the heavy lifting for clients to ensure the final design is maximized for user-centricity. We also ensure complete data privacy for customers. Book a demo today and take a test run for yourself.


.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20Image%201%20(22).png)
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%202%20(21).png)
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%203%20(20).png)