Gone are the days of designing based on gut feelings or what looks cool. Now, it's all about data – the real deal on how people actually interact with your creations. Data-driven design is like a key that unlocks the door and allows one to look at user actions. It takes all those clicks, taps, and scrolls and translates them into ways that ultimately tell how good or bad your design is.
A Data-driven design uses both qualitative and quantitative information to guide and shape digital product decisions. Despite any designer's level of expertise, collecting and studying data on customer preferences is an important factor in developing a product or service that fits customers' needs.
The Importance of Data in Modern Design Practices
Using data for insights has become a necessity. Users' behavior and preferences collected through user research directly determine the design process, which leads to the creation of more efficient and user-friendly products.
Here's why data is a game-changer for modern design:
1. Enhanced Decision-making
Companies can now analyze customers’ behaviors in terms of how they handle designs. Try visualizing an e-commerce checkout process refinement. Using data-driven design, you can analyze user behavior data, such as carts abandoned at specific stages of the checkout process. Such information identifies the problems and gives solutions.
Companies have a range of techniques to consider when making good decisions during the designing process: user research, A/B testing, data analytics, and feedback loops. It minimizes the possibility of miscalculations and thereby enhances the aesthetic quality of the design.
2. User-Centric Designs
Data helps identify customer preferences, needs, and behavior patterns, enabling businesses to develop designs that match their target users. Businesses try to comprehend trends in the collected data to improve design selection. For example, they may identify common navigation issues or feature preferences through clickstream analysis or A/B testing.
If data reveals that users frequently struggle to find specific information on a website, designers can adjust the information architecture to make it more intuitive and user-friendly.
3. Competitive Advantage
The design space is highly competitive when it comes to capturing customer attention. Imagine two companies launching similar apps. While company A relies on internal assumptions, company B leverages user testing data to identify pain points in competitor apps. This allows company B to develop a more attractive and user-friendly interface, which leads it to the top of the competition.
Key Principles of Data-Driven Design
Data-driven design involves several fundamental principles by which designers try to keep their designs aligned. We will take a closer look at these influencing factors.
- Start With Clear Objectives: Setting clear goals for your design is crucial before diving into data analysis. What task would you like your website, app, or product to accomplish for users? Is it to sign up for a newsletter, download an eBook, or make a purchase? A clear purpose is useful in helping you gather the most relevant data and further advance the business model that is likely to contribute to these milestones.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Data-driven design uses an iterative process that includes refining the design after each experience and then learning everything that was not anticipated while making improvements. This cycle helps fit designs accordingly to meet overall consumer satisfaction. For instance, the company gathers user feedback, takes in the statistics data, and uses the insights it has gathered to positively impact the product's usability.
.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%201%20(19).png)
- Integration of Quantitative and Qualitative Data: High-performing data-driven design combines the power of both quantitative data (numbers and metrics) and qualitative data (user feedback and observations) to ensure maximum engagement. This combined approach gives businesses a complete picture of how users interact with their design.
The Role of User Data in Informing Design Decisions
Data-driven design relies heavily on user data and for a good reason! Here's how user data fuels better design decisions:
1. Behavioral Metrics
Behavioral analytics metrics provide quantitative data about user behavior on your website or app. They track how users scroll, where they click or tap, and what activities they (or do not) take as a group. Designers use this data to analyze user interest, optimize design flow and navigation, and reduce friction points to make informed design decisions. For example, an e-commerce website notices that users spend more time on product pages with high-quality images.
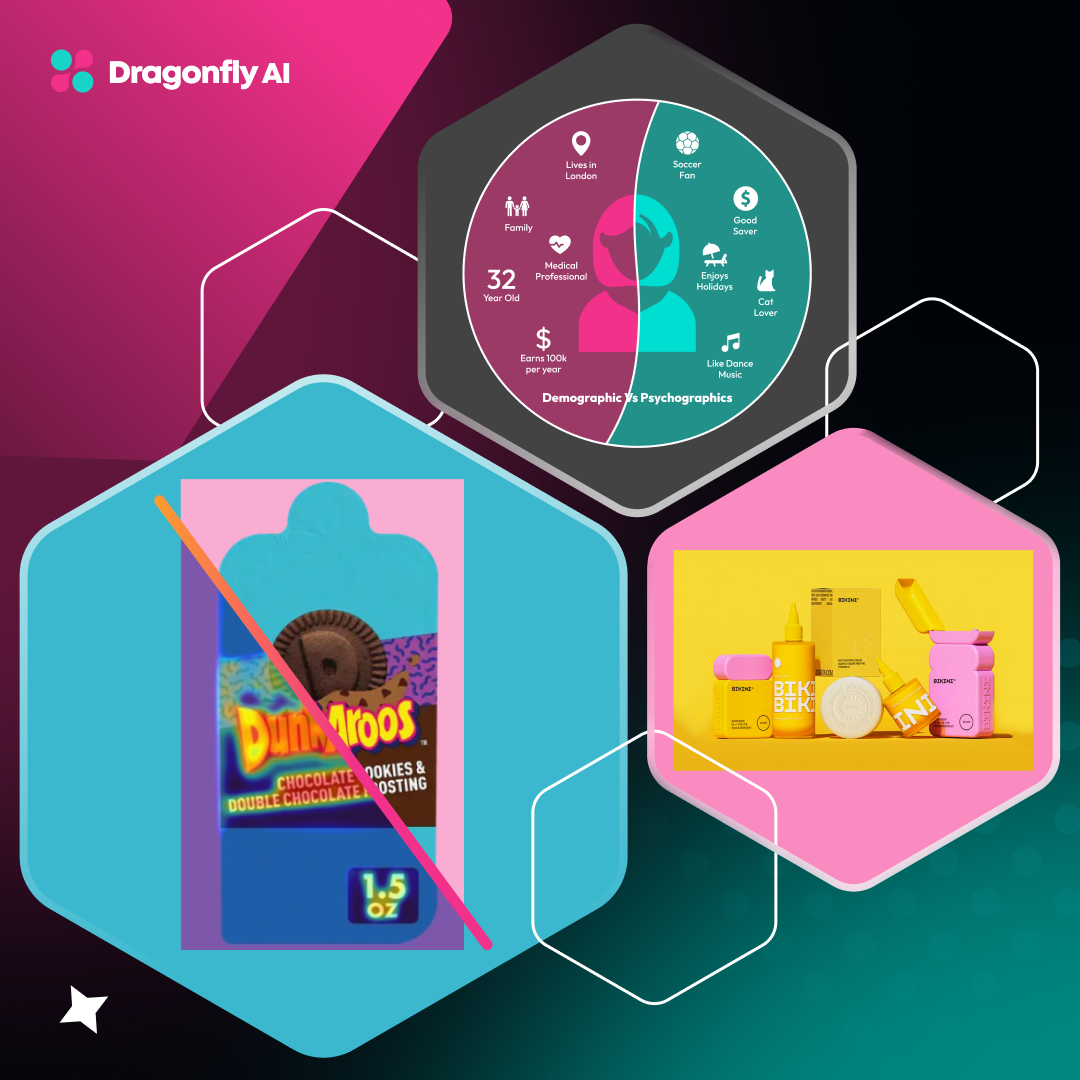
2. Demographic Insights
User data also offers valuable demographic insights that help designers understand their target audience better. By understanding demographic characteristics like age and location, designers can create designs that align with specific user segments. For instance, a travel agency may customize its website interface to cater to the sensibilities of different age groups or geographical locations to boost engagement.
3. Feedback and Surveys
Direct user feedback through surveys and interviews is essential to creating an optimal user experience (UX) through an effective user interface (UI). For example, if a fitness app receives consistent feedback that users find the workout instructions confusing, it would prompt the designers to revisit the clarity and user-friendliness of the instructions.
Hence, by incorporating user feedback throughout the design process, businesses can ensure data-driven UX/UI design that caters to the needs and preferences of their target audience.
Implementing Data-Driven Design in Your Workflow
Integrating data-driven design into your workflow requires a systematic approach. There are several methods to enhancing your data-driven design thinking, some of them are given below:
1. Data Collection Methods
The data-driven design approach uses various data collection techniques to influence and affect design decisions in digital product development. Businesses can use analytics tools to track user interactions and behavior on their digital platforms. They can also conduct A/B testing to compare design variations and determine which performs better regarding user engagement and conversion rates.
Moreover, businesses can organize user testing sessions to gather qualitative feedback directly from their target audience to understand preferences and challenges firsthand.
2. Data Analysis Techniques
Once you have your data, it's time to analyze it! Businesses can use heatmaps to visualize user interactions by highlighting areas of high and low engagement and identifying which design elements attract the most attention.
They can also use conversion funnels to track user journeys from entry to conversion, pinpointing where users drop off and guiding optimization efforts or sentiment analysis to gauge user sentiment through text analysis, revealing how users feel about your product or service.
3. Actionable Insights
The key to data-driven design is transforming data findings into actionable changes. Identify patterns and trends in the data to prioritize design improvements that address user needs and roadblocks. For example, if analytics reveal that users struggle to find specific information on your website, consider redesigning the navigation menu for improved accessibility.
In software design, user feedback can simplify complex workflows, and using data visualization tools can enhance data accessibility and usefulness. Ongoing design improvement with data-driven insights empowers one to establish products and experiences that synergize with the audience and the business.
Examples of Data-Driven Design Decisions
Data-driven design isn't just about collecting data – it's about using it to create better experiences. The following are some real-world examples of data-driven design in action:
1. Website Redesign
Imagine a website with a confusing layout and a lower conversion rate. The data-driven design comes to the rescue! Using tools like heatmaps, designers can see which elements are getting attention and what's getting ignored. For example, Flos, facing low checkout conversions, analyzed user heatmaps and navigation patterns to identify usability problems. They optimized the layout of their website from the homepage to checkout, resulting in a 125% increase in conversions.
2. App Interface Update
The meditation app Headspace wanted to increase user retention. They analyzed user interaction data and discovered that new users were overwhelmed by the app's many features. Based on this data, they streamlined the UI to focus on core meditation exercises. This resulted in a significant increase in users reaching their meditation goals. Data-driven UI design can make your app more user-friendly and keep people engaged.
3. Personalization Features
E-commerce giant Amazon is renowned for its data-driven approach to personalization. By using customer data such as past purchases, browsing history, and demographic information, Amazon customizes the shopping experience for each user. For instance, Amazon famously uses its recommendation engine to suggest products under the "Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought" and "Recommended Items For You" sections.
-1.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%202%20(16)-1.png)
This personalized approach significantly boosts sales and fosters customer loyalty, demonstrating the power of data-driven design in driving business growth.
The Future of AI in Data-Driven Design
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize data-driven design even further:
1. Predictive User Experience Models
A/B testing can definitely help us compare different design options, but AI is transforming data-driven design by analyzing vast datasets and highlighting user behavior patterns. With AI-powered algorithms, designers can proactively tailor experiences to individual users, delivering personalized content and interfaces. For example, Spotify's Discover Weekly uses AI algorithms to analyze user listening habits and predict music preferences, providing personalized playlists.
2. Automated Design Adjustments
AI systems that can make real-time design adjustments based on user data inputs are in the early development phase, but significant progress is being made. By automating repetitive tasks and leveraging AI algorithms, businesses can deliver personalized experiences at scale while reducing costs. These systems augment human creativity, fostering innovation and differentiation in the marketplace.
3. Ethical Considerations
As AI continues to evolve in data-driven design, ethical considerations become paramount. Designers must be mindful of privacy concerns and potential biases in algorithmic decisions. For example, AI-powered systems may inadvertently perpetuate existing biases if not adequately trained and tested. Hence, it is important to ensure fairness and transparency when using AI in design processes. Additionally, prioritizing AI explainability, human oversight, and accessibility ensures responsible and inclusive design practices that benefit all users.
How Data-Driven Design Increases Sales
Data-driven design isn't just about creating beautiful interfaces but driving actual business results. Following are some ways it boosts your sales:
- Optimized User Journeys: Imagine an e-commerce store where users get lost trying to find a specific item. Using techniques like clickstream analysis, data-driven design can track user clicks to see these roadblocks. Further, by analyzing this data, designers can simplify the search function and product categories. This makes it easier for users to find what they need and checkout faster – less frustration, more sales!
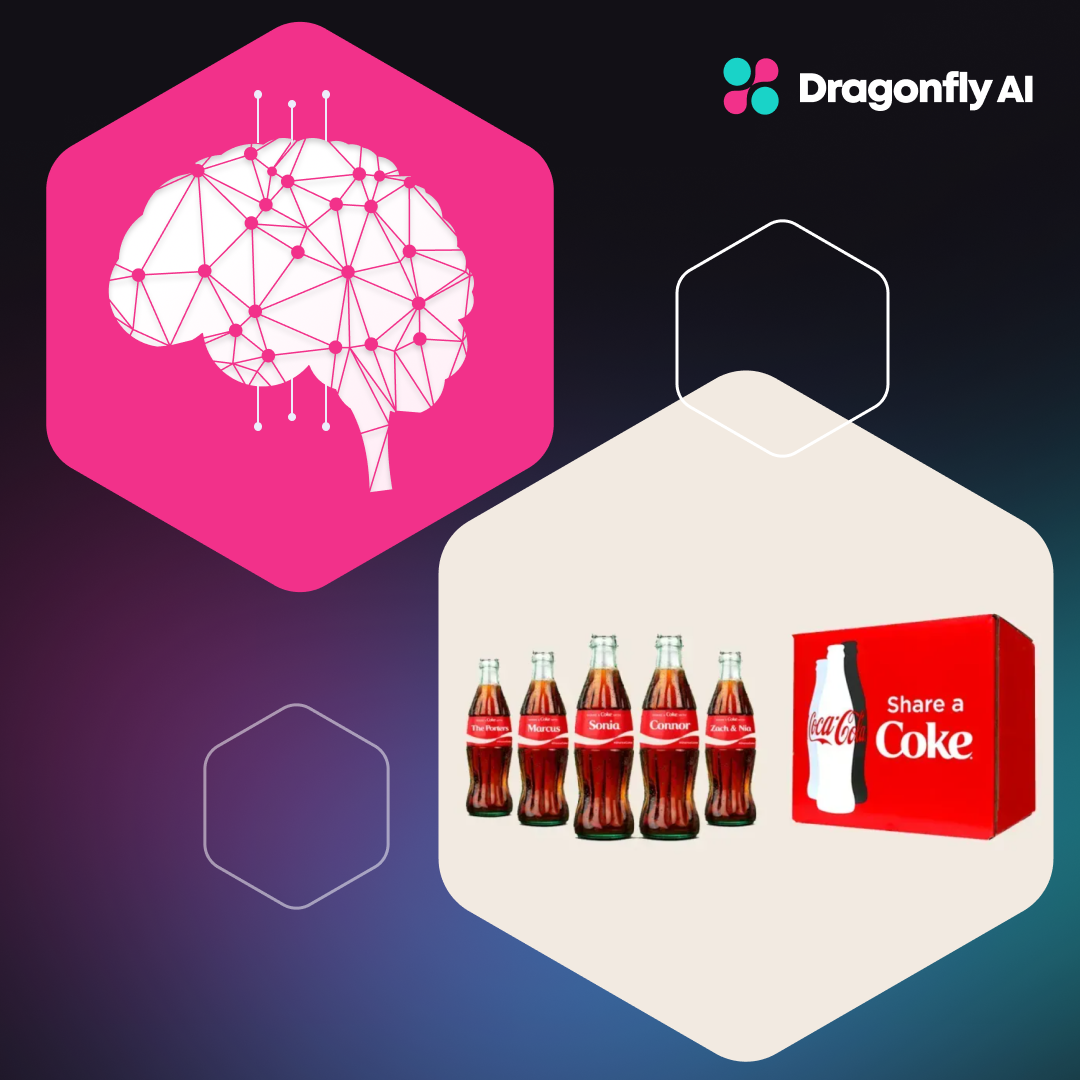
- Targeted Marketing and Personalization: Personalized content based on user data increases relevance and engagement. Netflix's recommendation system analyzes viewing history to suggest tailored content, resulting in higher viewer engagement and retention.
- Improved User Satisfaction and Loyalty: Feedback and behavior metrics data allow businesses to improve their design by understanding users’ pain points. They can achieve this through A/B testing different layouts or features to create optimal user experience. With the help of data-driven design thinking, businesses prioritize user satisfaction, foster loyalty, and encourage repeat purchases.
Conclusion
Data-driven design is not a trend but an absolute need in today’s digital environment. While data is invaluable, over-reliance on it may limit creativity and hinder innovation. Businesses should be aware of this problem and avoid becoming unduly confined by statistics, which might result in generic or unimaginative solutions.
Dragonfly AI offers a data-driven design approach that connects you with your target audience. Our predictive visual analytics technology assists brands in maintaining consistency and quality in visual design. Put your visual content to the test by speaking with our attention experts, and see how AI can help you find performance gaps.
Reach out to Dragonfly AI's attention experts and embark on a journey of discovery today!

.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%201%20(19).png)
-1.png?width=1280&height=700&name=Blog%20image%202%20(16)-1.png)
